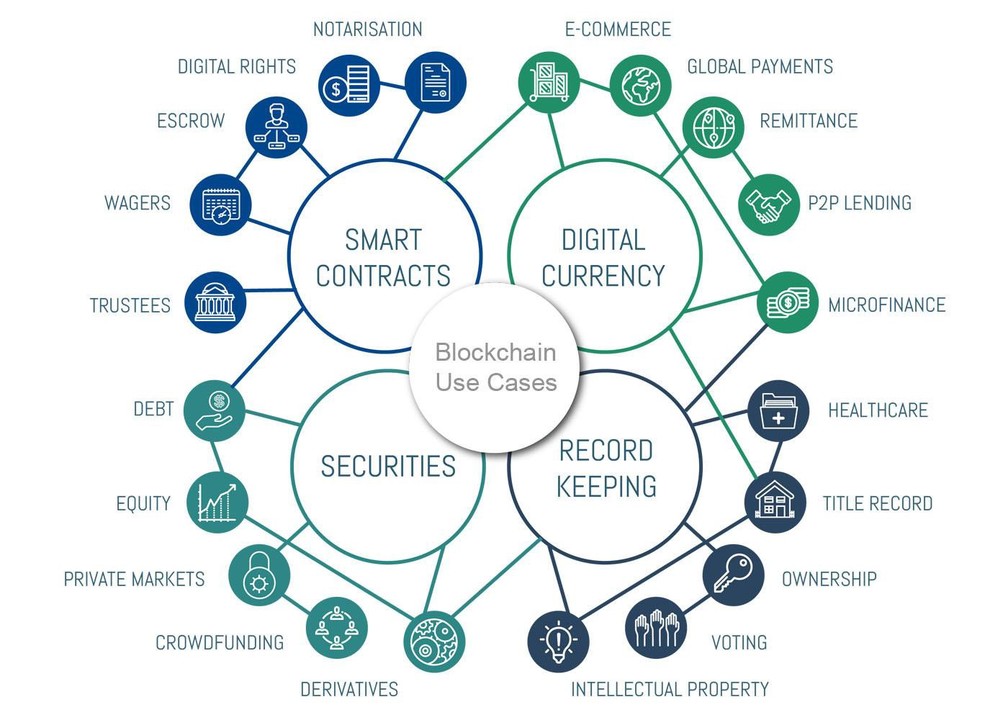
The modern financial system, with its intricate web of banking protocols, is a marvel of human achievement. Yet it is hamstrung by an intrinsic dependency on centralization. Decentralized Finance, or DeFi, aims to sever these dependencies by invoking the revolutionary principles of blockchain technology.
Introduction to DeFi
The Dawn of a New Financial Era
DeFi is a term that’s been creating waves in the financial sector, redefining the way we think about money and banking. At its core, DeFi refers to financial services that are built on blockchain technology, particularly Ethereum, and operate without the involvement of traditional financial intermediaries like banks, brokers, or insurance companies.
The Evolutionary Leap from Centralized Systems
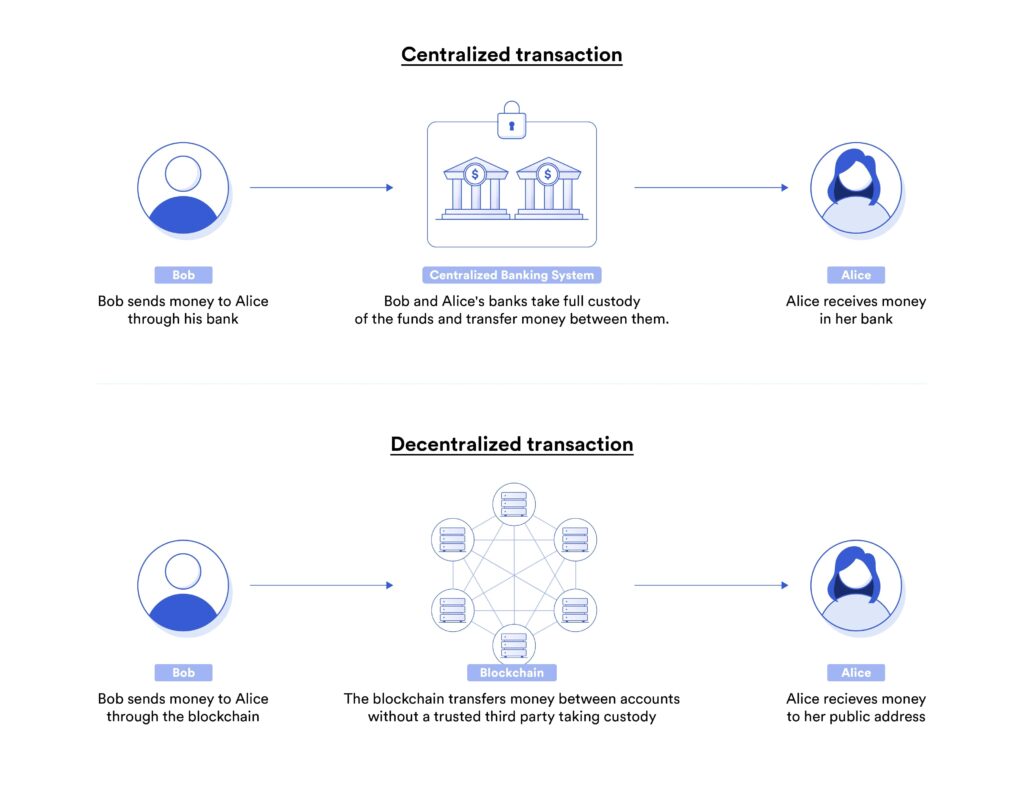
While centralized systems have provided reliability and scalability, they come with inherent drawbacks such as limited transparency and the concentration of power. In contrast, DeFi platforms are permissionless and transparent, ensuring that users have complete control over their assets.
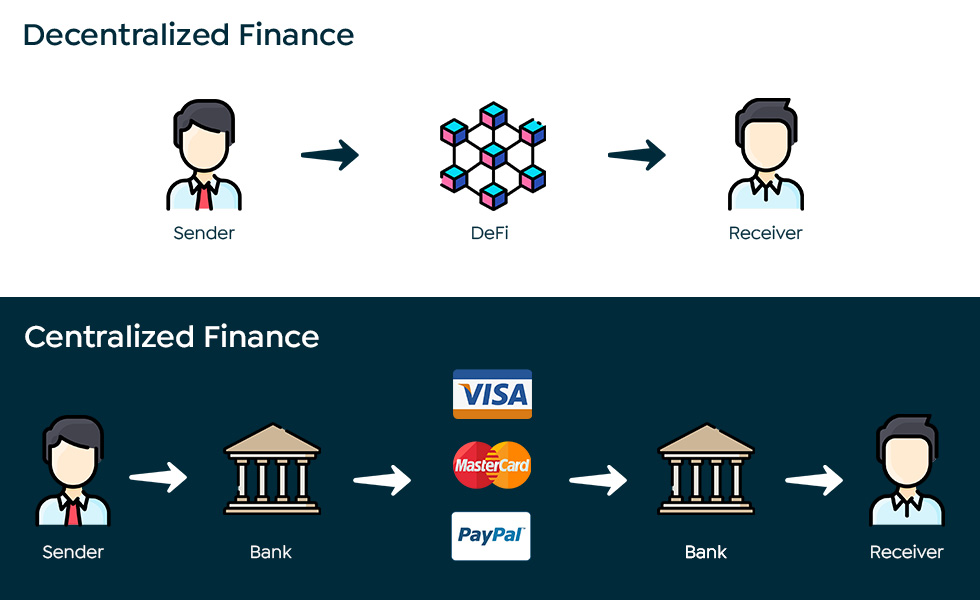
The Pillars of DeFi
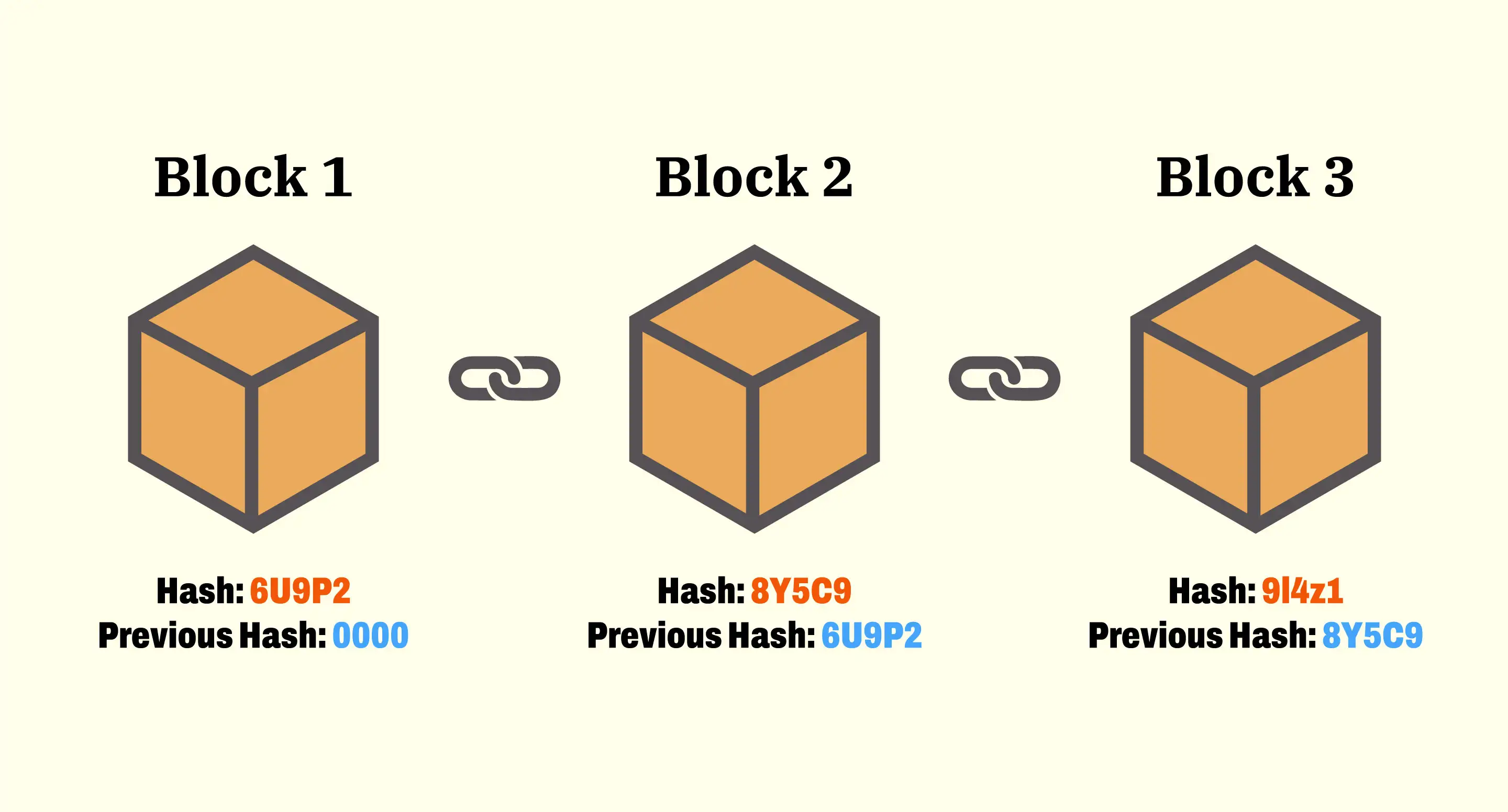
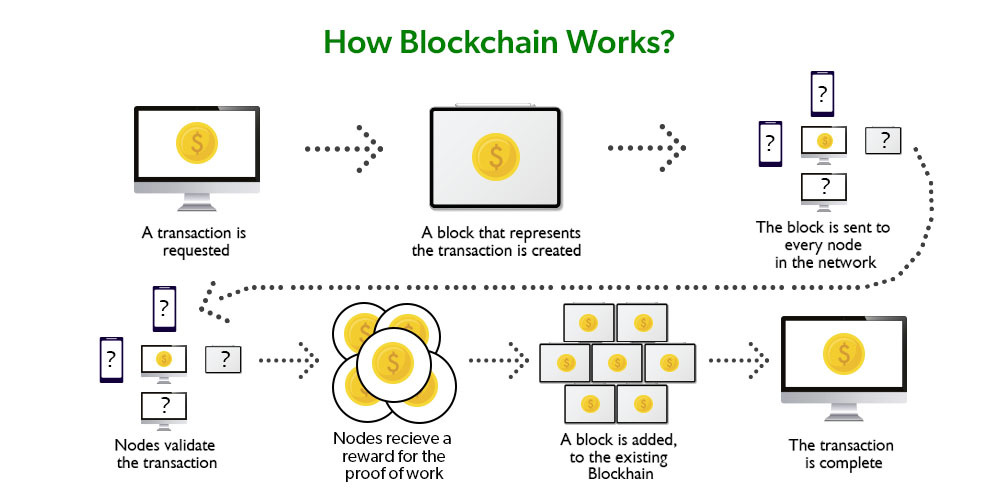
- Blockchain Technology: The backbone of DeFi is blockchain, a decentralized ledger that records all transactions transparently and securely. Ethereum, with its smart contract functionality, is the most widely used blockchain for DeFi applications.
- Smart Contracts: These are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code. They automate transactions and enforce agreements, eliminating the need for intermediaries.
- Decentralization: Unlike traditional finance, DeFi systems are not controlled by any single entity. They’re built on decentralized networks that offer more inclusivity and resilience against failures.
How DeFi is Changing the Game
Empowering Users
DeFi puts financial control back into the hands of users. You can lend, borrow, trade, invest, and even insure against risks directly through a DeFi platform without needing approval from a central authority.
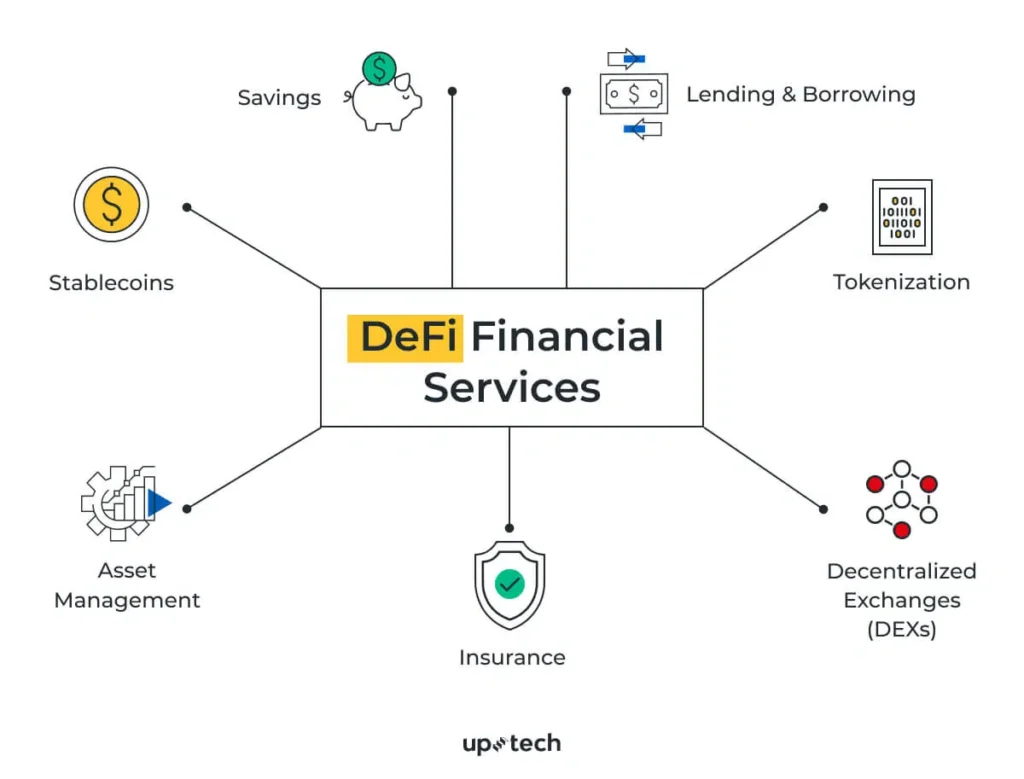
Accessibility and Inclusivity
DeFi makes financial services accessible to anyone with an internet connection, breaking down barriers that have traditionally excluded many from the financial system.
Popular DeFi Services
- Lending and Borrowing Platforms: Platforms like Aave and Compound allow users to lend their crypto assets or take out loans, earning or paying interest directly through smart contracts.
- Decentralized Exchanges (DEXs): Unlike traditional exchanges, DEXs like Uniswap allow for direct peer-to-peer trading of cryptocurrencies without an intermediary.
- Yield Farming and Liquidity Mining: Users can provide liquidity to DeFi platforms and earn rewards in the form of transaction fees or platform tokens.
The Mechanics of DeFi
Understanding Smart Contracts
At the heart of every DeFi application are smart contracts. These automated contracts execute pre-set conditions without human intervention, ensuring transactions are processed instantly and accurately.
The Role of Cryptocurrencies
To participate in DeFi, you need cryptocurrencies. Ether (ETH), the native currency of Ethereum, is commonly used, along with other digital assets and stablecoins like USDC or DAI.
Getting Started with DeFi
Setting Up a Digital Wallet
To interact with DeFi platforms, you’ll need a digital wallet like MetaMask, Trust Wallet, or Ledger. Wallets allow you to access your cryptocurrencies and connect you to various DeFi applications.
Engaging with DeFi Platforms
Once you have a wallet set up, you can start exploring various DeFi platforms. Always research and understand the services each platform offers and the risks involved.
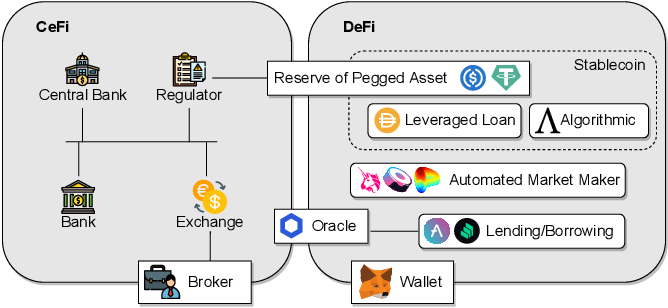
Risks and Challenges in DeFi
Smart Contract Risks
While smart contracts are efficient, they’re only as good as the code they’re written in. Bugs or vulnerabilities in smart contracts can lead to significant losses.
Market Volatility
The cryptocurrency market is known for its high volatility. This can impact DeFi services, especially those related to trading and lending.
Regulatory Uncertainty
The DeFi space is relatively new and still navigating the regulatory landscape. Changes in regulations can impact DeFi platforms and services.
The Future of DeFi
DeFi is not just a fleeting trend; it’s a glimpse into the future of finance. With continuous innovations and increasing interest from institutional investors, DeFi is poised for further growth. The potential for a more open, efficient, and inclusive financial system is enormous, making DeFi an area worth watching.
Conclusion
DeFi is revolutionizing the financial world, offering unprecedented access and control over financial services. For beginners, understanding and navigating this new terrain can be daunting, but the potential benefits are immense. As we move towards a more decentralized financial future, the opportunities in DeFi will continue to expand, opening doors for innovation, inclusivity, and financial empowerment.