This article aims to provide educational content and is not intended as investment advice.
Imagine standing in a never-ending line at the bank, the clock ticking away as you inch forward, just to get a simple transaction approved. There’s the cumbersome paperwork, the overworked bank staff, and the silent prayer that your request doesn’t get tangled up in bureaucratic red tape. We’ve all been there, entrusting our hard-earned money to institutions that require us to jump through hoops for every financial move.
Now, picture a world where these transactions happen almost magically, without the long lines, without the mountain of paperwork, and without the need to blindly trust an institution. Welcome to the world of smart contracts—a world where agreements execute themselves, trust is built into the code, and your digital wallet is your personal bank. Smart contracts are like having a banker, a lawyer, and a notary all rolled into one, working tirelessly for you 24/7, without the coffee breaks.
Traditional Contracts vs. Smart Contracts
Before diving into the digital realm, it’s crucial to appreciate what a contract, in its traditional form, represents. A contract is an agreement between two or more parties outlining specific actions and their associated conditions. Traditional contracts, while legally binding, often require third parties like lawyers or banks to ensure enforcement and validation. This not only adds to the complexity but also introduces additional costs and time delays. Smart contracts, by contrast, are self-executing contracts with the terms directly written into code.
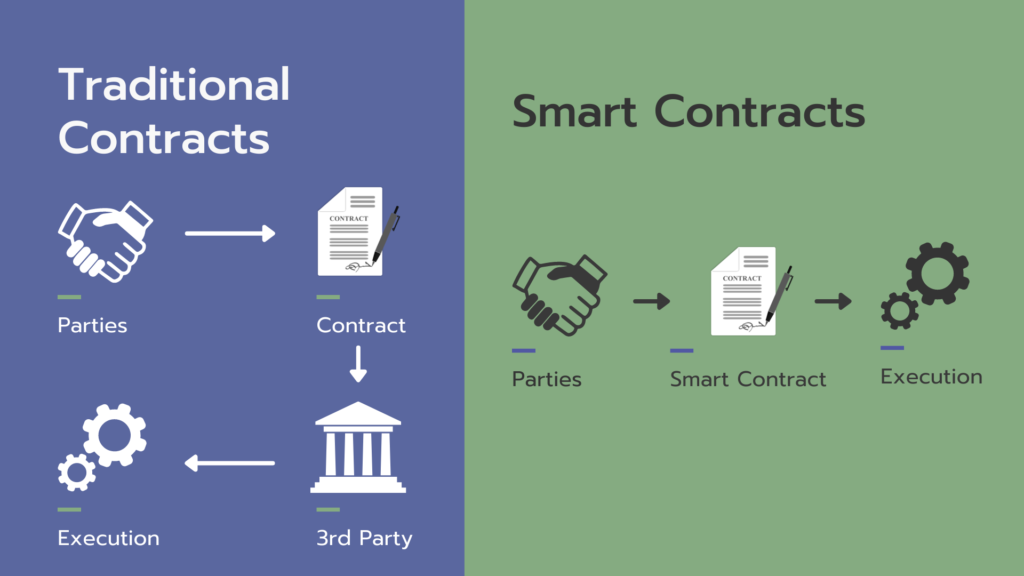
Operating on a blockchain—a decentralized digital ledger—smart contracts execute themselves when predefined conditions are met. They are lines of code, deployed on a blockchain, that automatically enforce their terms, making third-party oversight or verification generally unnecessary.
A Closer Look: The Mechanics of Smart Contracts
Smart contracts function on “if-then” programming logic. In other words, if a certain condition is met, then the contract will automatically execute the agreed-upon action. This code resides on a blockchain, providing the benefits of transparency, immutability, and security. Most commonly, smart contracts operate on platforms like Ethereum, which offer robust programming languages capable of executing complex contracts.
The Ethereum Ecosystem: A Smart Contract Haven
Ethereum, envisioned by Vitalik Buterin and launched in 2015, was designed not just as a cryptocurrency but as a platform for running smart contracts. While smart contracts can be deployed on various blockchains, Ethereum has become the most popular platform for them. Ethereum’s unique blockchain allows for the deployment of smart contracts via its Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM), a global computational engine that ensures these contracts are executed precisely as coded.
Why Smart Contracts Outshine Traditional Agreements
- Autonomy and Trust: Smart contracts remove the need for intermediaries. Once deployed, they execute automatically, reducing the potential for manipulation or errors. This autonomy builds trust among parties, as the contract will run as agreed without the possibility of external influence.
- Efficiency and Speed: The automation of smart contracts significantly cuts down the time it takes to complete contractual processes. Transactions and agreements that typically take days can be executed in a matter of minutes.
- Security and Reduction in Fraud: Being part of the Ethereum blockchain, smart contracts are encrypted and distributed across multiple nodes. This makes them highly secure and immune to fraud compared to traditional paper-based contracts.
- Cost-Effectiveness: By eliminating the need for middlemen like lawyers or notaries, smart contracts reduce transactional and operational costs. This is particularly beneficial for small businesses and individual entrepreneurs.
Use Cases: From Finance to Governance
Smart contracts have a plethora of applications, extending beyond financial transactions. In decentralized finance (DeFi), they facilitate lending, borrowing, and asset exchange without a central authority. Outside of finance, they are revolutionizing sectors like supply chain management, digital identity, and even electoral systems, providing a more transparent and efficient way to manage complex processes.
Getting Started: How to Interact with Smart Contracts
Interacting with smart contracts generally requires a digital wallet and some amount of cryptocurrency, often Ether if you’re using the Ethereum platform. Users can trigger smart contracts through various interfaces, including decentralized applications (dApps). Given their self-executing nature, understanding the terms is imperative before engaging with a smart contract.
Navigating Pitfalls: Due Diligence is Key
While smart contracts offer efficiency and transparency, they are not infallible. Code can have vulnerabilities, and once a contract is deployed on a blockchain, altering it can be incredibly difficult. Therefore, conducting thorough research and possibly seeking expert advice are advisable steps before entering into a smart contract.
Conclusion
Smart contracts on Ethereum, in addition to being a technological innovation, represent a shift towards a more efficient and transparent way of executing and enforcing agreements. By automating contractual obligations and reducing dependency on intermediaries, they offer a level of efficiency and security unprecedented in traditional contracts.
As the Ethereum ecosystem continues to grow, so does the potential of smart contracts, making them an indispensable tool in the digital age. For those embarking on their Ethereum journey, understanding and harnessing the power of smart contracts is a step into a world of unprecedented digital empowerment.
