Note: As a member of the PoolTogether Growth Team, my insights are drawn from my direct involvement with the project. This article aims to provide educational content and is not intended as investment advice.
Introduction
The journey to financial freedom is as old as currency itself, with individuals and societies constantly seeking secure ways to save and grow their wealth. In the quest for a balance between security and opportunity, an intriguing concept has emerged in the form of prize-linked savings accounts (PLSA). These accounts blend the thrill of winning with the prudence of saving, offering the chance to win prizes simply by saving money. This concept, which has been exemplified by the UK’s Premium Bonds, has found a new expression in the digital age through PoolTogether—a platform that embodies the ethos of prize-linked savings on the Ethereum blockchain.
The Inspiration – UK Premium Bonds
The UK’s National Savings and Investments (NS&I) Premium Bonds program, launched in 1956, stands as one of the most successful applications of the PLS concept. Premium Bonds allow individuals to purchase bonds and enter a monthly draw for tax-free prizes instead of receiving interest. With over £100 billion invested and around 21 million people participating, the program has become a staple of the UK’s savings landscape. The largest prize is £1 million, with odds of winning for each £1 bond number at 21,000 to 1 as of November 2023.

The success of Premium Bonds lies in their risk-free savings model with a bonus chance for rewards. Unlike a lottery, where one spends money with no guarantee of return, Premium Bonds safeguard the principal amount while providing the excitement of a potential win. This model has inspired several iterations globally (including Walmart’s Prize Savings Program), each aiming to make saving an engaging and rewarding experience.

Transition to Digital – The PoolTogether Model
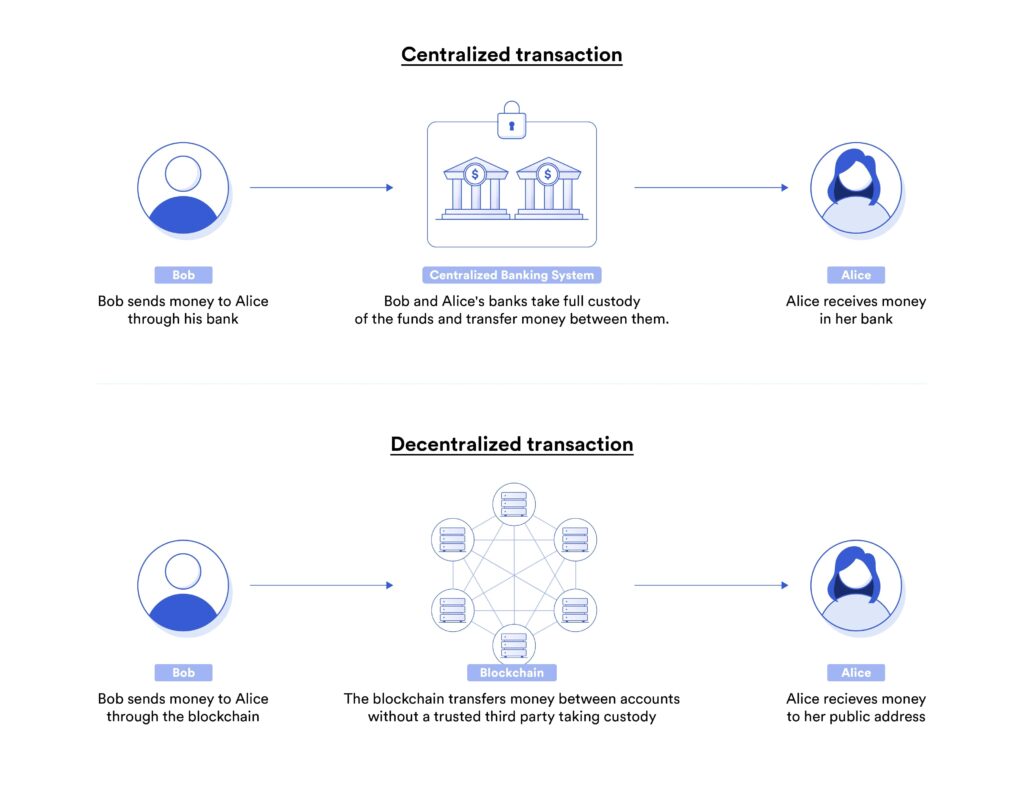
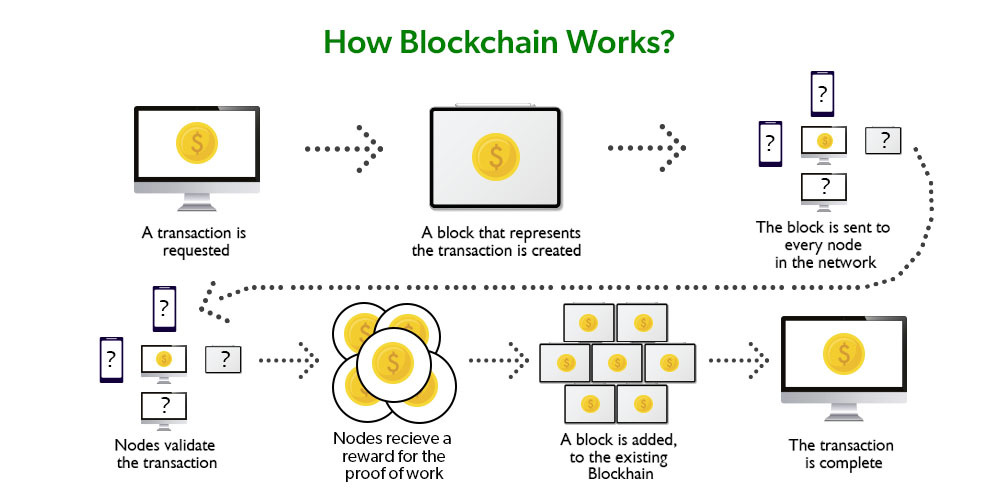
PoolTogether has harnessed the essence of Premium Bonds and repurposed it for the decentralized finance (DeFi) era. The platform is a blockchain-based protocol where users deposit cryptocurrency into a collective pool. This pool generates yield through other DeFi protocols, and instead of distributing this yield as interest, it is pooled and awarded as prizes in daily draws. This design ensures that even those who do not win retain their deposited funds, aligning with the foundational PLS principle of no-loss saving.
The Hyperstructure Advantage
The latest iteration of the platform, PoolTogether V5, also known as the Hyperstructure, represents a significant leap forward. It is an immutable and autonomous protocol, ensuring that once deployed, its rules and operations remain unchanged and free from any central control. This upgrade extends the core principle of PLS into a system that is open, transparent, and trustless—qualities that are central to the blockchain ethos.
By integrating the POOL token as the unified prize asset, PoolTogether V5 ensures scalability, deep prize liquidity, and stakeholder alignment. This system allows for the integration of an unlimited number of assets and yield sources, making it a robust and inclusive platform for prize savings.
Looking Ahead – The Impact of PoolTogether
PoolTogether’s Hyperstructure is more than just a technological innovation; it is a financial inclusion tool. It democratizes access to prize-linked savings, allowing anyone with an internet connection and some cryptocurrency to participate. This accessibility can be particularly impactful in regions with limited banking infrastructure, providing a secure and fun way for individuals to save and potentially earn significant rewards.
Moreover, the protocol’s permissionless nature fosters a collaborative and innovative environment where developers and entrepreneurs can build upon and extend its capabilities. From creating new vaults for various assets to designing hooks that integrate with other DeFi protocols, the possibilities for growth and development are vast.
Final Thoughts
PoolTogether stands at the intersection of traditional financial wisdom and cutting-edge blockchain technology. It reimagines the time-honored concept of prize-linked savings for a new generation, offering a model that is both secure and exhilarating. As the platform continues to evolve, it holds the promise of expanding financial freedom and empowering savers worldwide. With its roots in the tried and tested model of the UK’s Premium Bonds, PoolTogether is poised to define the future of saving.
How to Deposit to PoolTogether
- Getting Started with PoolTogether v5 Video Tutorial
- This is What Saving Looks Like: An Introduction to PoolTogether V5 Tutorial
PoolTogether Links & Resources
- Access V5 on app.cabana.fi or pooltime.app
- Discord
- Twitter, Farcaster, and Lens
- Blog
- Dev Docs