The mercurial world of cryptocurrencies often evokes awe and apprehension in equal measure, a realm where fortunes are minted and squandered overnight. Amid the volatility, a category of digital assets stands as an oasis of stability: the stablecoin. For the uninitiated, the term may sound paradoxical—a stable cryptocurrency? This guide demystifies stablecoins, detailing their mechanics, utility, and role in shaping a more inclusive and efficient financial system.
What is a Stablecoin?
A stablecoin is a type of cryptocurrency that is pegged to a stable asset, such as a traditional fiat currency like the U.S. Dollar or a commodity like gold. The primary objective is to mitigate the intrinsic volatility that characterizes cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum.
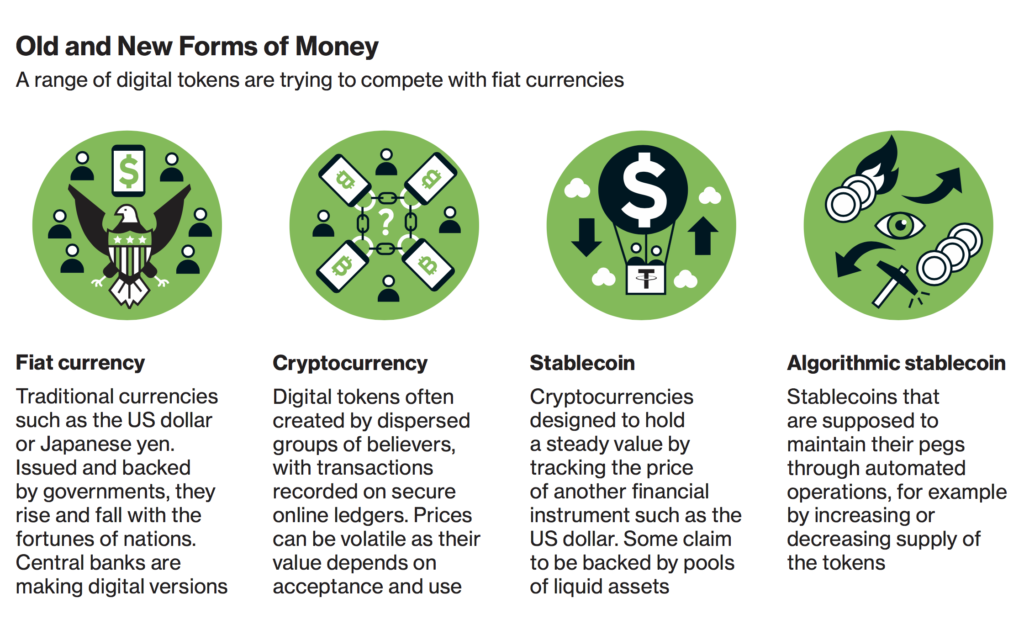
Types of Stablecoins
- Fiat-Collateralized: These stablecoins are backed by reserve assets held in traditional financial institutions. Popular examples include Tether (USDT) and USD Coin (USDC).
- Crypto-Collateralized: These rely on other cryptocurrencies as collateral but incorporate complex mechanisms to maintain their value. DAI is a prominent example.
- Algorithmic: These stablecoins are not backed by collateral but use algorithms to regulate supply and demand, maintaining their value.
The Importance of Stablecoins
- Volatility Hedge: Stablecoins offer a safe harbor during periods of extreme volatility in the crypto market.
- Payments and Remittances: Their stable value makes them ideal for transactions, particularly cross-border ones, without the fear of sudden price swings.
- Liquidity and Settlement: In Decentralized Finance (DeFi), stablecoins are often used as liquidity pools and for the settlement of smart contracts.
- Access to the Digital Economy: For unbanked populations, stablecoins offer a way to engage with digital financial services without a traditional bank account.

Risks and Considerations
- Regulatory Risk: The legal status of stablecoins is still a subject of ongoing debate, which can impact their stability.
- Counterparty Risk: For fiat-collateralized stablecoins, the stability depends on the reliability of the third-party holding the reserves.
- Complexity and Technical Risk: Crypto-collateralized and algorithmic stablecoins involve intricate systems that could be prone to errors or vulnerabilities.
How to Get Started With Stablecoins
- Research: Investigate different types of stablecoins, focusing on their underlying mechanisms and trustworthiness.
- Wallets and Exchanges: Utilize a reputable crypto wallet for storage and an established exchange for purchasing stablecoins.
- Use Cases: Experiment by utilizing stablecoins for specific applications like online payments, lending, or as a component in your investment portfolio.
The Takeaway
Stablecoins are a financial innovation and a bridge linking the realm of traditional finance and the frontier of digital assets. By providing stability in an otherwise volatile environment, they enable practical and everyday use of cryptocurrencies. For newcomers entering the cryptocurrency sphere, stablecoins represent both a sanctuary and a gateway—a secure and steady initiation into a financial future we are collectively scripting.
Stablecoins may appear as mere footnotes, but their utility and transformative potential are anything but trivial. Grasping the essence of stablecoins is integral for anyone keen to navigate the complexities and seize the opportunities of the digital financial world.
